Which medication is commonly prescribed for asthma control?

Inhaled corticosteroids are the most common long-term medication used to reduce airway inflammation in asthma patients.
What’s an effective way to reduce asthma attacks?
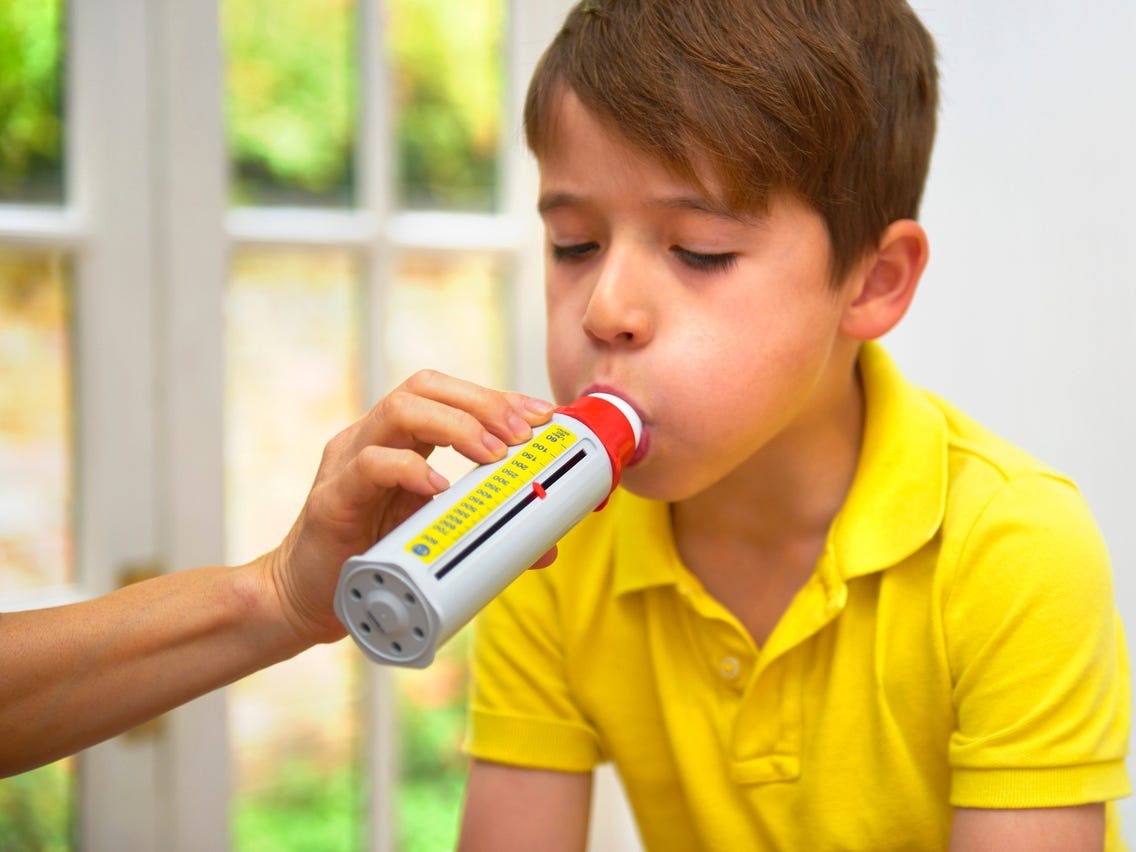

A peak flow meter helps measure lung function, allowing patients to monitor and manage their asthma more effectively.
What lifestyle habit helps prevent complications in diabetes?

Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels helps prevent complications by allowing patients to manage their diabetes more effectively.
Main lifestyle change for managing Type 2 diabetes?

Physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels and increases insulin sensitivity, key components in managing Type 2 diabetes.
Which diet is recommended to control high blood pressure?

The DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) emphasizes healthy eating with low salt intake to control blood pressure.
Which nutrient is important for hypertension control?

Potassium helps reduce the effects of sodium and relaxes blood vessels, which can lower blood pressure.
What’s the key method to monitor blood glucose levels in diabetes?
A glucometer is a portable device used to measure blood glucose levels, essential for diabetes management.
Chronic disease management refers to the ongoing care and support required for individuals living with long-term conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and asthma. These diseases often require lifelong attention and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life if not managed properly. Diabetes affects blood sugar regulation, hypertension pertains to high blood pressure, and asthma involves the narrowing of airways leading to breathing difficulties. Effective management is vital not only to control symptoms but also to prevent complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, or even death.
To successfully manage these conditions, healthcare providers must work closely with patients to develop long-term strategies. This includes regular check-ups, continuous monitoring, and the use of treatments tailored to individual needs. Disease management also helps reduce healthcare costs by preventing emergency interventions. With a focus on maintaining quality of life, chronic disease management is about proactive, rather than reactive, care.
Also Read: Preventive Healthcare: The Importance of Regular Check-Ups, Screenings, and Vaccinations
Personalized Treatment Plans
Personalized treatment plans are key in chronic disease management. Since every patient’s health profile, lifestyle, and severity of disease differ, healthcare providers must create individualized care strategies. For diabetes, this may include specific insulin regimens, whereas, for hypertension, a variety of medications can be tailored based on how the patient’s blood pressure responds. Asthma patients might require daily inhalers or quick-relief medications depending on symptom severity.
Effective management requires setting realistic goals that align with the patient’s abilities and lifestyle. For example, patients managing diabetes might work with their doctor to target specific blood sugar levels. In asthma care, goals could include reducing the frequency of attacks or improving lung function. This personalized approach fosters better patient engagement and promotes adherence to treatment plans, reducing the risk of complications.
Medication Management and Adherence
Medication management is critical in controlling chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and asthma. Proper medications not only control symptoms but also prevent the progression of the disease. Diabetes management often involves insulin or oral medications to regulate blood sugar levels. Hypertension is managed with medications like ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, or diuretics to lower blood pressure. Asthma treatment includes inhalers and, in severe cases, corticosteroids to maintain clear airways.
Medication adherence, however, remains a major challenge. Patients often miss doses or stop treatment due to side effects, forgetfulness, or even financial constraints. Strategies to improve adherence include educating patients on the importance of their medication, simplifying drug regimens, and using pill reminders or apps. Regular follow-ups help doctors assess whether the treatment is working or needs adjustment, ensuring continuous disease control and preventing flare-ups or emergencies.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing chronic diseases effectively. For diabetes, a healthy diet low in refined sugars and rich in fiber can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, improves insulin sensitivity and supports weight management. Hypertension can be controlled by reducing salt intake, managing stress, and engaging in daily exercise. Asthma patients can benefit from avoiding triggers such as allergens, pollution, or smoke while maintaining physical fitness to improve lung capacity.
Beyond diet and exercise, other lifestyle adjustments are equally important. Smoking cessation is essential for asthma and hypertension control, as it reduces airway inflammation and improves cardiovascular health. Limiting alcohol intake helps maintain healthy blood pressure and lowers diabetes risk. These lifestyle interventions empower patients to take control of their condition, complementing medical treatment for more comprehensive disease management.
Also Read: Physical Fitness Fundamentals: Exploring Exercise Types, Benefits, and Effective Workout Routines
Monitoring and Self-Management Tools
Regular monitoring and self-management are cornerstones of chronic disease control. Diabetics must frequently monitor blood sugar levels, either through finger-prick tests or continuous glucose monitors. Hypertensive patients need to track their blood pressure regularly, ensuring it remains within target ranges. Asthma patients benefit from using peak flow meters, which help them assess lung function and anticipate potential asthma attacks.
Modern technology has made self-management easier through mobile apps and wearable devices that track vitals, provide medication reminders, and store health data for future consultations. These tools enable patients to take an active role in their care, making real-time adjustments to their lifestyle or treatment plan when needed. Moreover, tracking symptoms and data improves communication with healthcare providers, allowing for quicker intervention when abnormalities arise.
Patient Education and Support Systems
Patient education is the foundation of chronic disease management. Understanding how their condition works and knowing the proper steps to take in managing symptoms empower patients to take control of their health. For example, diabetes education includes how to count carbohydrates, measure insulin, and recognize signs of hypoglycemia. Hypertension education focuses on the importance of regular monitoring and adhering to lifestyle changes. Asthma education involves recognizing early symptoms of flare-ups and knowing how to use inhalers correctly.
Support systems also play a critical role. Family members, caregivers, and healthcare professionals offer emotional and practical support, encouraging patients to follow their management plan. Peer support groups and online forums can also provide invaluable advice and encouragement. In some cases, mental health counseling is necessary, especially when dealing with the emotional burden of chronic illness. These support structures ensure that patients are never alone in their management journey, fostering long-term adherence and better health outcomes.
