What is the primary function of dietary fiber?

Fiber helps regulate the body's use of sugars and assists in digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
Which food is considered a good source of healthy fats?
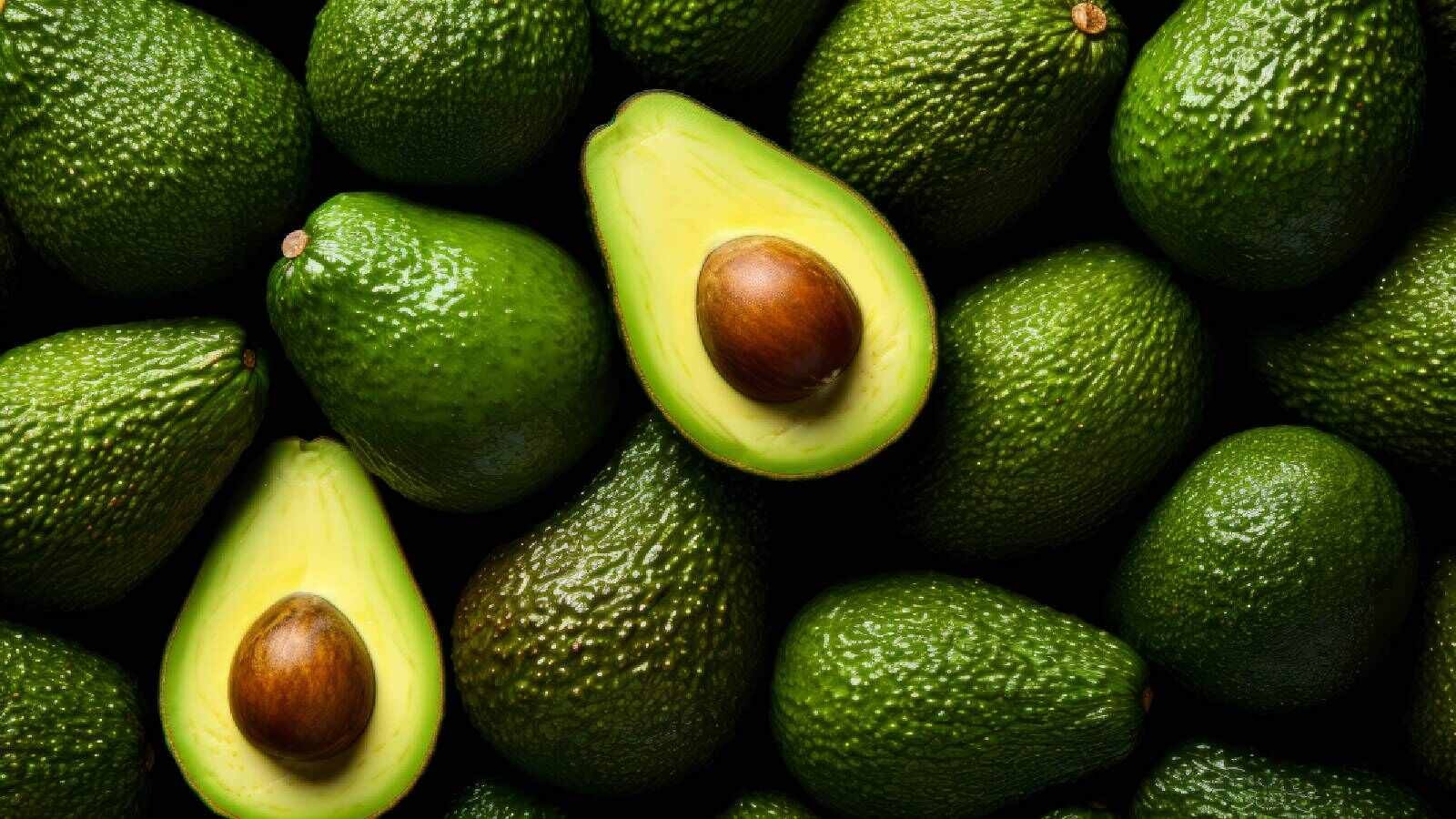

Avocados contain monounsaturated fats, which are heart-healthy fats that can help reduce bad cholesterol levels.
Which vitamin is crucial for maintaining healthy bones?
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is vital for maintaining strong bones and preventing bone-related diseases.
What is the recommended daily intake of water for most adults?

The general recommendation is to drink around 2 liters of water per day to stay hydrated, although individual needs can vary based on activity level and climate.
Which nutrient is essential for muscle repair and growth?
Proteins are the building blocks of muscle tissue and are essential for repair and growth, especially after physical activity.
What is the primary source of energy for the human body?

Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy, providing the necessary fuel for physical activity and proper organ function.
Which mineral is vital for oxygen transport in the blood?
Iron is a key component of hemoglobin in red blood cells, which helps transport oxygen throughout the body. Lack of iron can lead to fatigue and anemia.
What is the best dietary strategy for long-term weight management?

The best way to manage weight long-term is by following a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients and practicing portion control rather than extreme or restrictive diets.
Nutrition is the science that deals with how food affects the body’s functions and overall health. It involves the processes of ingestion, digestion, absorption, and metabolism of nutrients that the body needs to survive, grow, and function optimally. Proper nutrition is critical because the food we eat impacts almost every aspect of our well-being, from energy levels to disease prevention. Eating the right balance of nutrients is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, improving mental clarity, boosting immunity, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Key Components of Nutrition
Nutrition can be divided into two main categories: macronutrients and micronutrients. Macronutrients are the nutrients required by the body in large amounts, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for the body, especially the brain and muscles. They are found in foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. It’s essential to focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, which provide sustained energy, rather than refined sugars that cause blood sugar spikes.
Proteins play a crucial role in building and repairing tissues, including muscles, organs, and the immune system. Sources of protein include meat, fish, eggs, dairy, beans, and nuts. It’s important to consume a variety of protein sources to get all essential amino acids. Fats are another macronutrient vital for energy storage, insulation, and protecting organs. Healthy fats like those from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil support heart health, while trans fats and excessive saturated fats can lead to heart disease.
Principles of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet involves consuming a variety of foods in the right proportions to ensure the body gets all the necessary nutrients. One key principle is eating a wide range of foods, which ensures the intake of diverse nutrients. Each food group offers different essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients, so it’s important not to rely on a limited diet. For instance, leafy greens provide iron and calcium, while fruits offer vitamins and antioxidants.
Portion control is another fundamental principle. Even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain if eaten in excessive amounts. Maintaining portion control helps manage calorie intake and prevents overeating. Alongside portion control is the principle of moderation. While it’s okay to enjoy occasional treats, limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats is crucial to avoid excess calorie intake and potential health issues.
Special Dietary Considerations
Some individuals may follow special diets based on ethical, health, or medical reasons. Vegetarian and vegan diets, which exclude animal products to varying degrees, require careful planning to ensure all nutrient needs are met. Protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12 are nutrients of concern for those following these diets, but they can be obtained through plant-based sources such as legumes, fortified foods, and supplements.
Gluten-free diets are necessary for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Avoiding gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, requires careful attention to food labels and finding alternatives like quinoa, rice, and gluten-free flours. Ensuring a balanced diet in these circumstances can be challenging, but it’s possible with proper guidance.
Reading Food Labels and Understanding Ingredients
Understanding how to read food labels is a key aspect of maintaining a healthy diet. Food labels provide crucial information about the nutritional content of the product, helping consumers make informed decisions. The most important sections to review are serving sizes, calorie content, and the amounts of macronutrients like fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. Additionally, the label lists essential vitamins and minerals, offering a snapshot of the product’s nutrient density.
Many food products also contain hidden sugars, unhealthy fats, and additives that are not immediately obvious. Ingredients like high-fructose corn syrup, hydrogenated oils, and artificial preservatives can negatively impact health, even in foods marketed as “healthy.” It’s important to recognize these hidden ingredients and limit their intake.
Healthy Eating Habits and Practical Tips
Developing healthy eating habits goes beyond just choosing the right foods. Planning meals and preparing them at home is one of the best ways to ensure balanced, nutritious meals. By cooking at home, you have full control over the ingredients, portion sizes, and nutritional content of your food. This practice also helps avoid the hidden sugars, unhealthy fats, and excessive calories often found in restaurant and processed foods.
Snacking can be part of a healthy diet when done wisely. Opting for nutrient-rich snacks like fruits, nuts, yogurt, or vegetables ensures that your body gets a steady supply of energy and nutrients throughout the day without excessive calorie intake. On the other hand, processed snacks loaded with sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats should be avoided.
The Role of Physical Activity in a Healthy Lifestyle
Physical activity and nutrition go hand in hand in maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Exercise not only helps burn calories and control weight, but it also improves cardiovascular health, builds muscle strength, and enhances mental well-being. Regular physical activity also increases metabolism, helping the body process and utilize nutrients more effectively.
Different types of physical activities cater to various fitness levels and lifestyles. Aerobic exercises like walking, running, and swimming improve heart health, while strength training helps build and maintain muscle mass. Flexibility exercises like yoga enhance mobility and prevent injury, making them an essential part of a well-rounded fitness routine.
